In the first part of our series on Personalization, we discussed what personalization is and how it can benefit your business.
As you learn more about your visitors and develop your audience segmentation, you’ll be able to deliver increasingly personalized and relevant messages to each visitor. By understanding the different segments of your shoppers and variations in their behavior, you can identify their needs, increase engagement on your site, facilitate their decision-making process in your store, and increase the likelihood of turning browsers into buyers.
There are several things you can do to create personalized on-site experiences . The challenge doesn’t lie in integrating them all, but in selecting the personalization strategies that are right for your business and most effective at serving relevant content, products, and offers to your shoppers.
Read on to learn more about the 5 main approaches to personalization, ordered according to their level of personalization (Deciding on a Personalization Strategy).
1. Content and Product-related Personalization Strategies
Content and Product-related personalization strategies are based on the assumption that the immediate viewing behavior is an indicator of current interest. The goal is to continuously serve relevant content to your shoppers to encourage browsing and increase their time on your site. A typical implementations of this approach is “You viewed X, you might also like Y”.
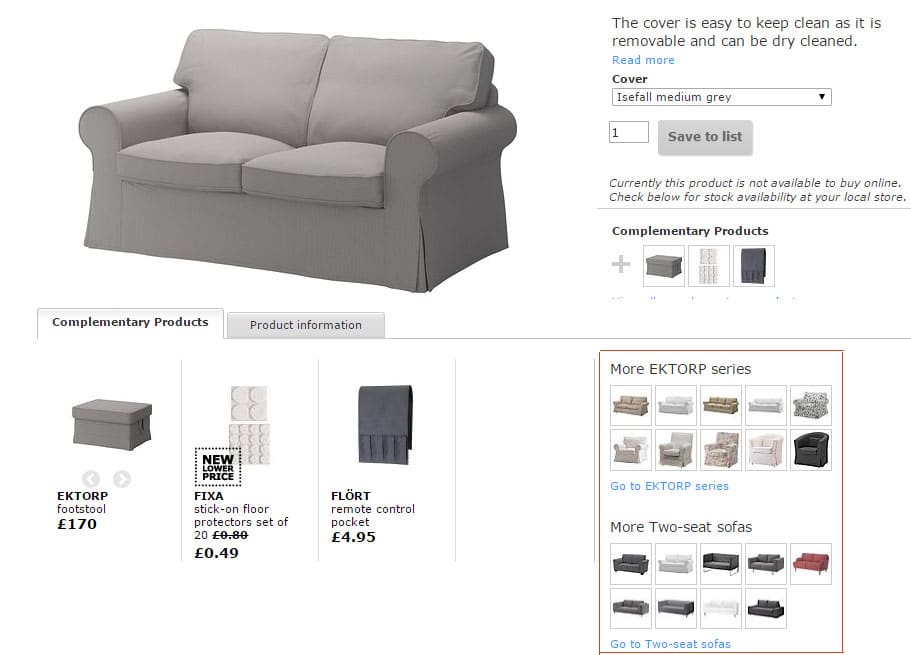
Displaying similar products based on brand and product type to encourage further browsing
Content and Product-related personalization can be easily implemented, as long as they found on a sound classification and structured definition of products and product meta-data. These strategies work by generating product and content recommendations based on product similarity in fields that are relevant to shoppers such as brand, product type or color.
More personalized approaches are able to display related products from different product categories (e.g., suggesting suitable helmets to shoppers who are currently viewing bikes), and take the browsing history (Click paths in session) or previous purchases into account to suggest the next best offer (e.g. suggesting a bike computer instead of a helmet, if the user has already bought a helmet before).
As Content and Product-related personalization approaches are generally product-centric and not necessarily user-centric, they define a more basic form of personalization. However, they prove very effective where there is no prior information about shoppers or in environments where new products have a short life-cycle and new products are added constantly.
2. Trigger-based Personalization Strategies
Trigger-based Personalization strategies are one of the easiest types of personalization. Before implementing this strategy, it is necessary to define and identify key milestones that should trigger specified follow-up actions.
The most common example for this personalization method is Personalized retargeting, where visitors went to a website and looked at Product X, left the website and are served targeted messages that are contextually related to the product they have viewed previously. These messages can be displayed in the form of an ad, an email or directly on the website before the user leaves or at their next visit.
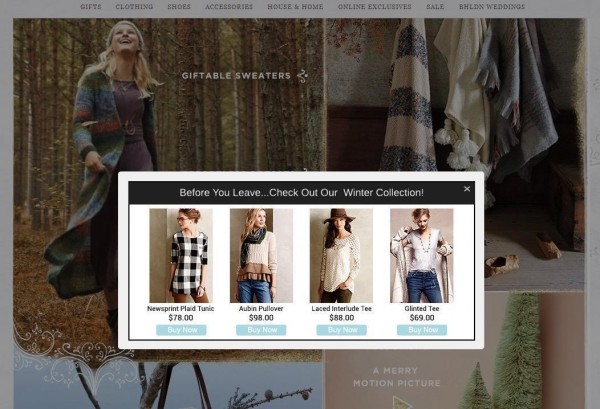
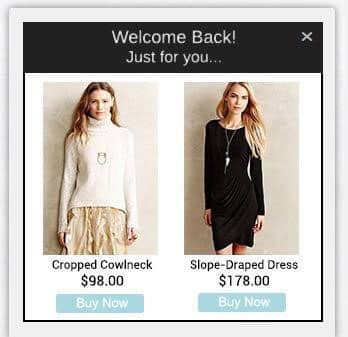
Trigger-based strategies require prior knowledge about the target audience, their sales cycle and the behaviors that drive them through your sales cycle. You can build a matrix of touch points that lets you reach out at critical moments.
More complex trigger-based approaches look at a sequence of visitor interactions and the dwell time in a defined amount of time (time before your shoppers click and pick a different product) to provide for a higher form of personalization. However, these complex methods are also complicated to set up, because you will have to apply suitable measures to take care of removing behavioral noise (e.g., longer viewing times due to external distractions like shoppers taking a call in between browsing).
Trigger-based methods work best if you can combine your follow-up action with a compelling, personalized offer that captures your visitor’s attention and is of value to them.
3. Time and Event-based Personalization Strategies
These strategies identify your shoppers’ preferences based on interaction cues, demographic information or external factors such as seasons, geo-location or time of day, to personalize the website dynamically (Dynamic content).
Examples for this personalization strategy are changing the default currency automatically or displaying products according to known preference.
Another interesting form of application is detecting the shopper’s location, the device used to browse your site, and the time of day, to push relevant, individual in-store offers to their mobile phone.
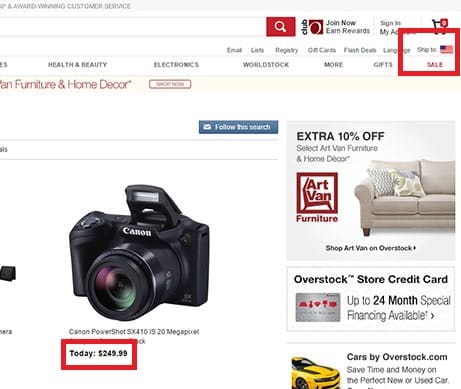
Identifying the user’s location and changing the content dynamically
These strategies may sound simple, however, they are powerful, very impactful, and effective at delivering a personalized experience. Visitors are able to notice them immediately and benefit from more streamlined browsing and purchase processes. Just imagine how off-putting it can be for visitors, if they have to change the language or the currency every time they visit your store.
4. Crowd-Sourcing Personalization Strategies
Crowd-sourcing personalization strategies make use of the voice and the behavior of many shoppers to suggest products and content to individual visitors in order to drive engagement. The most common representation of this method are “Most viewed products”, “Most bought products”, or “Most liked product” lists.
These People-matching and Nearest Audience Strategies prove to be very effective means to serve potentially interesting content and work best on websites that experience a substantial amount of traffic.
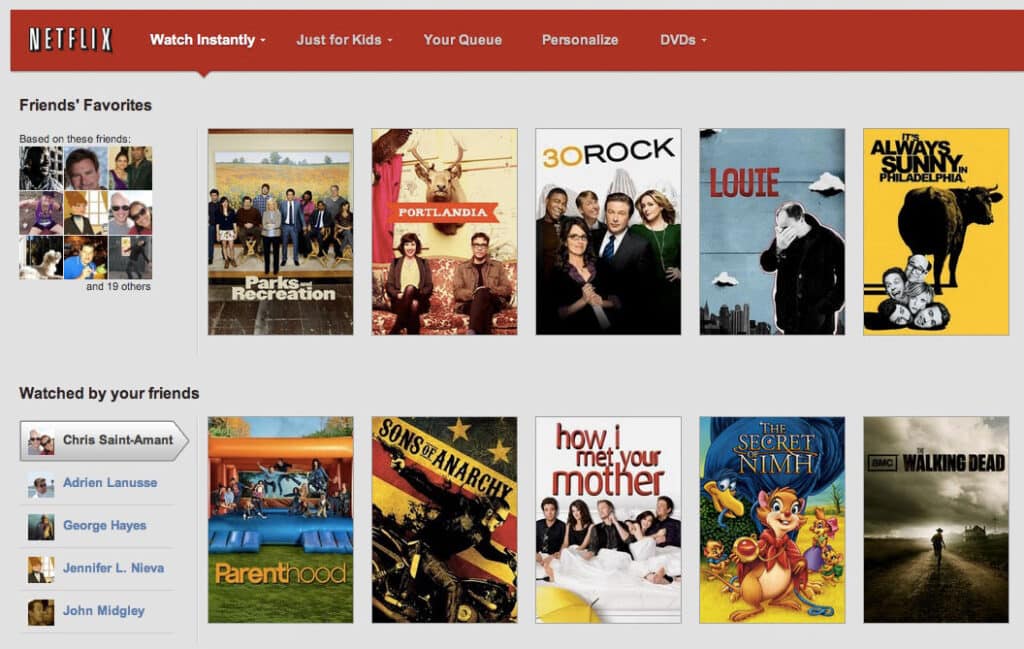
More sophisticated methods segment shoppers and create shopper personas to group similar shoppers based on previous behavior (visitor frequency), location, device, interest (browsing or purchase history), demographic information, shopper profiles or social associations between users such as friend-based personalization.
5. User-Directed Personalization Strategies
User-Directed Strategies are the highest form of personalization as they found on a better understanding of shoppers interest, lifestyle, attitudes and opinions. As the suggestions are driven by explicit user input, these methods are able to deliver an undeniably personal experience.
Product configurators, Product finders, Product advisors, and other Guided selling approaches are most effective examples for user-directed personalization strategies: users answer a sequence of questions and receive targeted product recommendations based on their selection.
This strategy is especially helpful in situations where the decision-making process is complex – for example, when purchasing complex products with many features and functions. It is also valuable when selling products that are new to the marketplace and in situations where the intended audience is not likely to have knowledge of a product domain.
Online shoppers are easily confused by an overload of product and purchase information. Directing your customers toward identifying the most interesting and valuable information, saves them money and time. Whenever done well, user-directed personalization strategies can stand in the center of personalization activities, as they open up the opportunity to offer truly personalized 360° shopping experiences and can generate valuable data and actionable insights to further improve other personalization tactics.
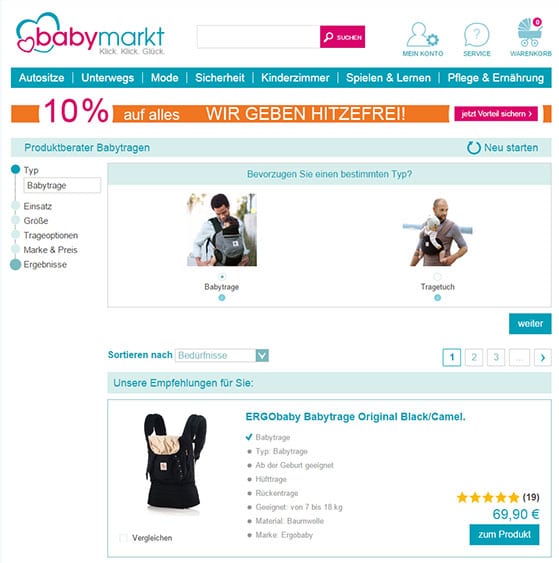
Example of a Guided selling product finder solution – Users answer a few questions in a need-oriented questionnaire and receive personal recommendations with the most suitable baby carriers – Found at http.//www.baby-markt.de.
The most ideal application area for user-directed personalization are mobile devices, whose limited space and typical form of use make mobile a natural platform for the integration of Guided selling to create fluid and personal experiences.
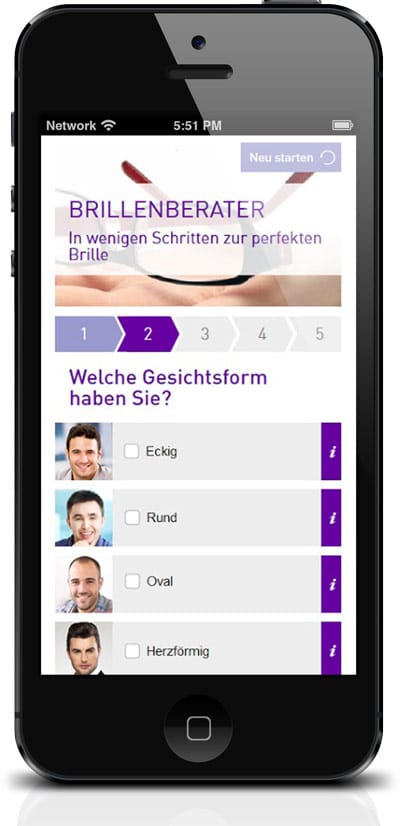
Found on brille24.de
I hope this article gave you a bit of an insight on the most common personalization methods. There are many ways you can go with and not every one of them may be appropriate for you individual case and business needs. Remember, it is not about the technology you use, but about how you combine strategies to align your personalization approaches with your business goals and most importantly with your shopper’s expectations.
Personalization is critical to the success of your business and it’s important to get started. You are more likely to ensure returning visitors, if you use customer preferences (explicit or implicit) to help your shoppers narrow down the product choices.
Your turn. Which personalization strategies do you integrate and what works best for you? Let us know




